spring security
SpringSecurity
[!note]
- SpringSecurity是一个功能强大且可高度定制的身份验证和访问控制框架,是基于Spring的应用程序的实施标准。
- SpringSecurity是一个专注为应用程序提供身份验证和授权的框架。与所有Spring项目一样,SpringScurity的真正强大之处在于可以轻松扩展以满足自定义的要求
- 官方文档: https://spring.io/projects/spring-security#overview
- 功能:
- 身份认证(authentication):身份认证是验证
谁正在访问系统资源,判断用户是否为合法用户。认证用户的常见方式是要求用户输入用户名和密码。 - 授权(authorization):用户进行身份认证后,系统会控制
谁能访问哪些资源,这个过程叫做授权。用户无法访问没有权限的资源。 - 防御常见攻击(protection against common attacks):CSRF、HTTP Headers、HTTP Requests
- 身份认证(authentication):身份认证是验证
1. SCI
=== AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer是 Spring Security提供的SCI
- AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer引导 SpringSecurity 过滤链注册
-
AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer
public abstract class AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {private static final String SERVLET_CONTEXT_PREFIX = "org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.CONTEXT.";public static final String DEFAULT_FILTER_NAME = "springSecurityFilterChain";private final Class<?>[] configurationClasses;protected AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer() {this.configurationClasses = null;}protected AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer(Class<?>... configurationClasses) {this.configurationClasses = configurationClasses;}public final void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) {this.beforeSpringSecurityFilterChain(servletContext);if (this.configurationClasses != null) {AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext rootAppContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();rootAppContext.register(this.configurationClasses);servletContext.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext));}if (this.enableHttpSessionEventPublisher()) {servletContext.addListener("org.springframework.security.web.session.HttpSessionEventPublisher");}servletContext.setSessionTrackingModes(this.getSessionTrackingModes());this.insertSpringSecurityFilterChain(servletContext);this.afterSpringSecurityFilterChain(servletContext);}protected boolean enableHttpSessionEventPublisher() {return false;}private void insertSpringSecurityFilterChain(ServletContext servletContext) {String filterName = "springSecurityFilterChain";DelegatingFilterProxy springSecurityFilterChain = new DelegatingFilterProxy(filterName);String contextAttribute = this.getWebApplicationContextAttribute();if (contextAttribute != null) {springSecurityFilterChain.setContextAttribute(contextAttribute);}this.registerFilter(servletContext, true, filterName, springSecurityFilterChain);}protected final void insertFilters(ServletContext servletContext, Filter... filters) {this.registerFilters(servletContext, true, filters);}protected final void appendFilters(ServletContext servletContext, Filter... filters) {this.registerFilters(servletContext, false, filters);}private void registerFilters(ServletContext servletContext, boolean insertBeforeOtherFilters, Filter... filters) {Assert.notEmpty(filters, "filters cannot be null or empty");Filter[] var4 = filters;int var5 = filters.length;for(int var6 = 0; var6 < var5; ++var6) {Filter filter = var4[var6];Assert.notNull(filter, () -> {return "filters cannot contain null values. Got " + Arrays.asList(filters);});String filterName = Conventions.getVariableName(filter);this.registerFilter(servletContext, insertBeforeOtherFilters, filterName, filter);}}private void registerFilter(ServletContext servletContext, boolean insertBeforeOtherFilters, String filterName, Filter filter) {FilterRegistration.Dynamic registration = servletContext.addFilter(filterName, filter);Assert.state(registration != null, () -> {return "Duplicate Filter registration for '" + filterName + "'. Check to ensure the Filter is only configured once.";});registration.setAsyncSupported(this.isAsyncSecuritySupported());EnumSet<DispatcherType> dispatcherTypes = this.getSecurityDispatcherTypes();registration.addMappingForUrlPatterns(dispatcherTypes, !insertBeforeOtherFilters, new String[]{"/*"});}private String getWebApplicationContextAttribute() {String dispatcherServletName = this.getDispatcherWebApplicationContextSuffix();return dispatcherServletName == null ? null : "org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.CONTEXT." + dispatcherServletName;}protected Set<SessionTrackingMode> getSessionTrackingModes() {return EnumSet.of(SessionTrackingMode.COOKIE);}protected String getDispatcherWebApplicationContextSuffix() {return null;}protected void beforeSpringSecurityFilterChain(ServletContext servletContext) {}protected void afterSpringSecurityFilterChain(ServletContext servletContext) {}protected EnumSet<DispatcherType> getSecurityDispatcherTypes() {return EnumSet.of(DispatcherType.REQUEST, DispatcherType.ERROR, DispatcherType.ASYNC, DispatcherType.FORWARD, DispatcherType.INCLUDE);}protected boolean isAsyncSecuritySupported() {return true;}} -
SpringWebSecurityConfiguration
@Configuration@EnableWebSecuritypublic class SpringWebSecurityConfiguration {// 默认配置// @Bean// public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {// http.authorizeHttpRequests((requests) -> requests.anyRequest().authenticated());// http.formLogin(withDefaults());// http.httpBasic(withDefaults());// return http.build();// }} -
SpringWebSecurityInitializer
package com.exmaple.web;import org.springframework.security.web.context.AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer;public class SpringWebSecurityInitializerextends AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer {public SpringWebSecurityInitializer() {super(SpringWebSecurityConfiguration.class);}}
2. 密码学
=== 密码加密主要分为 对称加密 和 非对称加密
- 对称加密:使用相同的密钥进行加密和解密
- 非对称加密:使用一对密钥,公钥用于加密 & 私钥用于解密
- MD5 (Message-Digest Algorithm) 常用于密码加密策略的控制及实现
2.1 散列算法策略
2.1.1 特征
- MD5 不可逆 不可根据运算结果 反推计算值(但是呢需要防止彩虹表)
- MD5 多次运算相同计算值 总是得到相同的结果 不同计算值总是得到不同的结果 【算法稳定】
2.1.2 策略
- 根据 MD5 算法特征 需要为计算值加入随即盐 及 MD5(计算值 + 随即盐) = 计算结果
- 无法进行逆运算 即 校验需要二次加密 计算值比对两次结果
-
逻辑
加密原始值A1 + 随机盐 => 运算结果A11校验原始值A2 + 随机盐 => 运算结果A22比较结果A11 <=> 结果A22 是否相同 即可得出 原始值A1 > 原始值A2 是否相同注意点原始值A2 加密 需要获取 原始值A1 所使用 随机盐
2.2 MD5
=== java.security.MessageDigest 提供散列算法实现
2.3 spring-security crypto
=== spring-security-crypto 模块提供加密抽象及实现
3. RBAC权限模型
=== 一般权限模型基于 RBAC(Role-Base Access Controller) 可以根据业务对以下五个表进行调整
-
user
CREATE TABLE user (user_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,user_nickname VARCHAR(20),user_username VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,user_password VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,user_gender INT,user_phone VARCHAR(12) NOT NULL,); -
role
CREATE TABLE role (role_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,role_name VARCHAR(20)); -
user_role
CREATE TABLE user_role (ur_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,ur_user_id INT NOT NULL,ur_role_id INT NOT NULL); -
permission
CREATE TABLE permission (permission_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,permission_name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL); -
role_permission
CREATE TABLE role_permission (rp_id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,rp_role_id INT NOT NULL,rp_permission_idd INT NOT NULL,);
4. Spring Security 权限模型
=== Spring Security 权限模型由 UserDetails | GrantedAuthority 构成
- org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority : 角色权限
- org.springframework.security.core.userDetails.UserDetails : 表示用户信息
- org.springframework.security.core.userDetails.UserDetailsService : 获取用户信息
4.1 GrantedAuthority
=== 一个GrantedAuthority对象表示一个角色 | 权限 【Spring Security】 不区分权限角色
- Spring Security 只有权限集合的概念 不区分你抽象的是角色还是权限,只是在乎你有没有
-
GrantedAuthority
public interface GrantedAuthority extends Serializable {String getAuthority();}
4.2 UserDetails
=== Spring Security 权限模型中的用户信息
-
UserDetails
/** Copyright 2004, 2005, 2006 Acegi Technology Pty Limited** Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.* You may obtain a copy of the License at** https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0** Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and* limitations under the License.*/package org.springframework.security.core.userdetails;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.Collection;import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority;/*** Provides core user information.** <p>* Implementations are not used directly by Spring Security for security purposes. They* simply store user information which is later encapsulated into {@link Authentication}* objects. This allows non-security related user information (such as email addresses,* telephone numbers etc) to be stored in a convenient location.* <p>* Concrete implementations must take particular care to ensure the non-null contract* detailed for each method is enforced. See* {@link org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User} for a reference* implementation (which you might like to extend or use in your code).** @author Ben Alex* @see UserDetailsService* @see UserCache*/public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {/*** Returns the authorities granted to the user. Cannot return <code>null</code>.* @return the authorities, sorted by natural key (never <code>null</code>)*/Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();/*** Returns the password used to authenticate the user.* @return the password*/String getPassword();/*** Returns the username used to authenticate the user. Cannot return* <code>null</code>.* @return the username (never <code>null</code>)*/String getUsername();/*** Indicates whether the user's account has expired. An expired account cannot be* authenticated.* @return <code>true</code> if the user's account is valid (ie non-expired),* <code>false</code> if no longer valid (ie expired)*/boolean isAccountNonExpired();/*** Indicates whether the user is locked or unlocked. A locked user cannot be* authenticated.* @return <code>true</code> if the user is not locked, <code>false</code> otherwise*/boolean isAccountNonLocked();/*** Indicates whether the user's credentials (password) has expired. Expired* credentials prevent authentication.* @return <code>true</code> if the user's credentials are valid (ie non-expired),* <code>false</code> if no longer valid (ie expired)*/boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();/*** Indicates whether the user is enabled or disabled. A disabled user cannot be* authenticated.* @return <code>true</code> if the user is enabled, <code>false</code> otherwise*/boolean isEnabled();}
4.3 UserDetailsService
=== 根据用户名获取用户信息并转为 UserDetails 标准用户信息接口 [可不使用]
-
UserDetailsService
package org.springframework.security.core.userdetails;/*** Core interface which loads user-specific data.* <p>* It is used throughout the framework as a user DAO and is the strategy used by the* {@link org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider* DaoAuthenticationProvider}.** <p>* The interface requires only one read-only method, which simplifies support for new* data-access strategies.** @author Ben Alex* @see org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.DaoAuthenticationProvider* @see UserDetails*/public interface UserDetailsService {/*** Locates the user based on the username. In the actual implementation, the search* may possibly be case sensitive, or case insensitive depending on how the* implementation instance is configured. In this case, the <code>UserDetails</code>* object that comes back may have a username that is of a different case than what* was actually requested..* @param username the username identifying the user whose data is required.* @return a fully populated user record (never <code>null</code>)* @throws UsernameNotFoundException if the user could not be found or the user has no* GrantedAuthority*/UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException;}
5. EnableXXXXXXBeanConfiguration注解
=== Spring框架给出两种 【动态】 装配Bean机制 选择式动态 | 运行时动态
- 选择式动态 由 开发者主要通过 @Import 注解封装完成 【被选择Bean配置不要被扫描】
- 运行时动态 由 Spring @Conditional 条件注解完成,可在运行时决定装配 Bean
EnableXXXXBeanConfiguration可实现可插拔式配置
-
@EnableWebSecurity
@Import实现装配
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@Documented@Import({ WebSecurityConfiguration.class, SpringWebMvcImportSelector.class, OAuth2ImportSelector.class,HttpSecurityConfiguration.class })@EnableGlobalAuthenticationpublic @interface EnableWebSecurity {/*** Controls debugging support for Spring Security. Default is false.* @return if true, enables debug support with Spring Security*/boolean debug() default false;}
6. 认证流程
=== 认证流程 是指用户登录之后记录登录标识,下次请求时根据会话跟踪获取用户信息的过程
服务器认证:
- 资源服务器认证授权:负责保护资源并验证访问令牌
- 认证服务器: 负责验证用户凭据并发放访问令牌
6.1 三个基本组件
6.1.1 AuthenticationManager
[!note]
认证管理器:定义了Spring Security 过滤器要如何执行过滤操作,AuthenticationManager 认证成功之后会返回一个Authenticationd对象,这个Authentication对象会被设置到SecurityContextHolder中。
6.1.2 AuthenticationProvider
[!note]
Spring Security 支持多种不同的认证方式,不同的认证方式对应不同的身份类型,AuthenticationProvider就是针对不同的身份类型执行具体的身份认证。例如,常见的 DaoAuthenticationProvider 用来支持用户名/密码登录认证。
- authenticate方法用来执行具体的身份验证。
- supports方法用来判断当前AuthenticationProvider是否支持对应的身份类型。
6.1.3 ProviderManager
ProviderManager 和 AuthenticationProvider 之间的关系
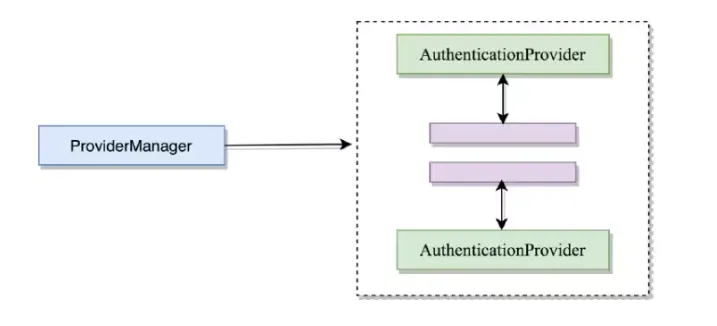
[!note]
在Spring Security中,由于系统可能同时支持多种不同的认证方式,例如同时支持用户名 /密码认证、RememberMe认证、手机号码动态认证等,而不同的认证方式对应了不同的 AuthenticationProvider,所以一个完整的认证流程可能由多个AuthenticationProvider来提供。
多个AuthenticationProvider将组成一个列表,这个列表将由ProviderManager代理。换句话说,在 ProviderManager 中存在一个 AuthenticationProvider 列表,在 ProviderManager 中遍历列表中的每一个AuthenticationProvider去执行身份认证,最终得到认证结果。
6.2 流程
- 当用户提交登录请求时,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter会从当前请求 HttpServletRequest中提取出登录用户名/密码,然后创建出一个 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 对象。
- UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 对象将被传入 ProviderManager 中进行具体的认证操作。
- 如果认证失败,则SecurityContextHolder中相关信息将被清除,登录失败回调也会被调用。
- 如果认证成功,则会进行登录信息存储、Session并发处理、登录成功事件发布以及登录成功方法回调等操作。
6.3 系统资源权限设计
=== 系统资源权限一般分为三种情况 【不受限】 【登录权限】 【角色权限】
留言评论